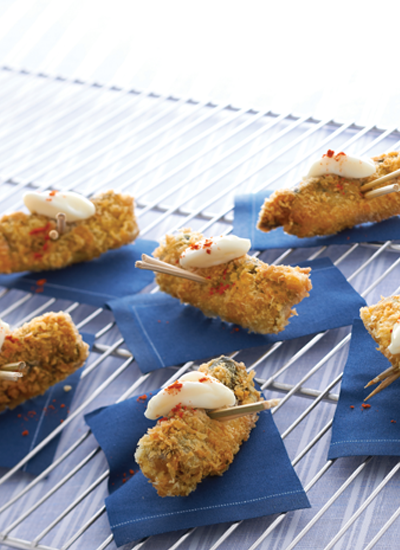
Coconut Milk Benefits
Coconut Milk Benefits
Based on the book FOOD FOR THE BRAIN by Professor Shirasawa PHD, an anti-aging physician, ISBN 978-967-14205-0-8.
Benefits of consuming coconut milk It is similar to coconut oil.
Lauric acid is one of the ingredients in coconut milk. where it is converted to a useful antiviral and antibacterial agent in the body called monolaurin. This helps destroy a wide range of pathogenic organisms. Therefore, it is believed that consuming coconut milk may help protect the body from infections and viruses.
Also, coconut milk does not contain lactose. Therefore, it is a good substitute for cow's milk for people with lactose intolerance.
It is naturally high in nutritional value. Rich in fiber, vitamins C, E, B1, B3, B5 and B6.
and minerals such as iron, selenium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and phosphorus.
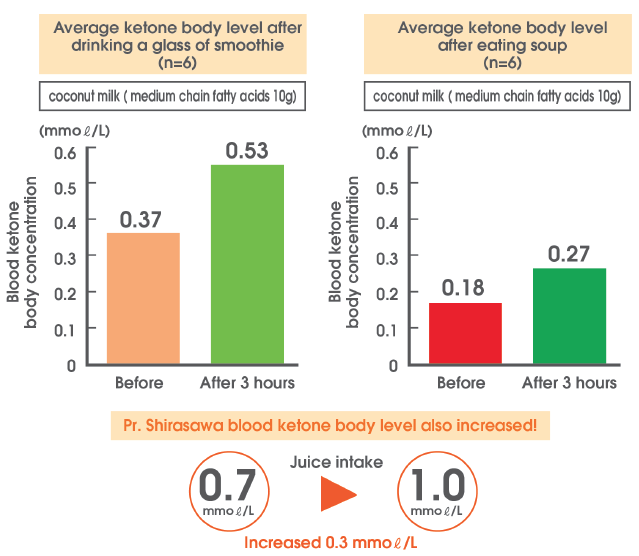
As part of the research on coconut milk in Japan Professor Shirasawa conducted a study on the effects of coconut milk on ketone levels in the body. The study included 12 volunteers, divided into two groups, with all ketone levels measured on an empty stomach.
The first group of 6 volunteers all had a carrot smoothie with coconut milk, while the other 6 had oyster soup cooked with coconut milk.
Both formulas had the same amount of 66 grams of coconut milk, which was converted to 10 grams of medium chain fatty acids (MCFAs) after 3 hours and ketone levels were measured again, as shown in Figure 3 on the left: Smooth. The carrots on the right are oyster soup, the orange column indicates the levels of ketones on an empty stomach. The green column is the level 3 hours after coconut milk consumption. In both groups, the results could confirm that ketone levels were increased after eating coconut milk.

in further testing Compared drinking coffee with coconut oil. with coffee with coconut milk In both drinks there is the same amount of coffee. One cup of coffee was filled with 2 tablespoons of coconut milk (30 grams per 5 grams of medium-chain fatty acids) and another cup was filled with 1 tablespoon of coconut oil (15 grams per 10 medium-chain fatty acids). gram).
at the same blood sugar level of 0.2 mmol/L. After four hours of drinking coffee, ketone levels rose to 4 mmol/L in coconut milk coffee. and increased to 0.4 mmol/L. In coffee mixed with coconut oil.
This experiment showed that coconut milk was more effective than coconut oil at increasing ketone levels.
One of the advantages of coconut milk over coconut oil is the calorie count.
100 g of coconut oil provides 900 kcal of energy, while 100 g of coconut milk provides only 245 kcal.
As you can see, coconut milk yields better results. Especially for people who want to lose weight quickly.
"All above text are direct quotes from Prof. Shirasawa book and they are presented here for information about the latest findings about coconut benefits. These information can not be seen as a recommendation to modify or alter a medical treatment. Like any other good food ingredient , coconut can bring benefits only within a proper balanced diet and regular physical exercises."
Reference: FOOD FOR THE BRAIN - PROF. SHIRASAWA'S READINGS














 To understand why coconut fat stands out And that's amazing Therefore it is necessary to understand the properties. and how the body reacts to it.
To understand why coconut fat stands out And that's amazing Therefore it is necessary to understand the properties. and how the body reacts to it.